CASIO ESSENTIAL MATERIALS

CASIO
ESSENTIAL
MATERIALS
CASIO ESSENTIAL MATERIALS
CASIO original teaching materials specialized for fx-991CW
Total number of pages: 900 pages or more
Covers all high school units
- Even beginners can start classes using scientific calculators.
- You can make full use of the functions of the scientific calculator for each learning item
- With detailed explanation using keylog display
- Simple and easy-to-read design
- Comes with practice questions that students can try on their own
If you register with CASIO ID MEMBERS, you can download CASIO ESSENTIAL MATERIALS for free.
*If you are not registered with a CASIO ID MEMBERS, you will not be able to download CASIO ESSENTIAL MATERIALS.
Features of this book
The teaching materials were developed to communicate the appeal of scientific calculators to teachers and students. They aim to change awareness and enhance learning efficiency in mathematics by minimizing time spent on manual calculations, reducing aversion to complex math. These materials also promote diversification in learning and problem-solving methods, particularly beneficial for real-life scenarios with complex values. Lastly, creative use of various calculator functions facilitates a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts, encouraging exploratory learning and visualization of numerical values through tables without the need for listing or numbering.
Scientific Calculator Basics & Beyond
As well as providing first-time scientific calculator users with opportunities to learn basic scientific calculator functions from the ground up, the book also has material to show people who already use scientific calculators the appeal of scientific calculators described above.
Exploring CASIO Calculator Functions
You can also learn about functions and techniques that are not available on conventional Casio models or other brands of scientific calculators.
High School Math Covered
This book covers many units of high school mathematics, allowing students to learn how to use the scientific calculator as they study each topic.
Classroom to Homework
This book can be used in a variety of situations, from classroom activities to independent study and homework by students.
Structure

1
TARGET
This book covers many units of high school mathematics, allowing students to learn how to use the scientific calculator as they study each topic.
2
STUDY GUIDE
Mathematical theorems and concepts are explained in detail. A scientific calculator is used to check and derive formulas according to the topic.

3
EXERCISE
Students learn basic examples based on the explanation provided in the Study Guide.
4
check
Explains how to use the scientific calculator to solve and calculate problems.
5
PRACTICE
Students can do practice problems similar to those in EXERCISE. They can also practice using the scientific calculator, applying what they learned in the check sections.

6
ADVANCED
Practical problems have been included in several topics. Solutions using a scientific calculator are also presented as necessary.

We also have a PowerPoint version available to project on a screen for use in class.
Table of contents
- 01 Algebraic Expressions and Linear Inequalities
- Addition and subtraction of expressions
- Expanding expressions (1)
- Expanding expressions (2)
- Expanding expressions (3)
- Factorization (1)
- Factorization (2)
- Factorization (3)
- Factorization (4)
- Expanding and factorizing cubic polynomials
- Real numbers
- Absolute values
- Calculating expressions that include root signs (1)
- Calculating expressions that include root signs (2)
- Calculating expressions that include root signs (3)
- Linear inequalities (1)
- Linear inequalities (2)
- Simultaneous inequalities
- Equations and inequalities with absolute values
- 02 Quadratic Functions
- Quadratic functions
- Quadratic function graphs (1)
- Quadratic function graphs (2)
- Quadratic function graphs (3)
- Quadratic function graphs (4)
- Determining equations of quadratic functions
- Maximums and minimums of quadratic functions (1)
- Maximums and minimums of quadratic functions (2)
- Maximums and minimums of quadratic functions (3)
- Maximums and minimums of quadratic functions (4)
- Common points on the x axis of graphs of quadratic functions (1)
- Common points on the x axis of graphs of quadratic functions (2)
- Common points on parabolas and lines
- Quadratic inequalities
- Conditions under which quadratic inequalities have solutions
- Conditions to solve quadratic equations
- 03 Trigonometry
- Defining a trigonometric ratio
- Finding a side
- Finding an angle
- Relation between sine and cosine
- Trigonometric ratio formula including tangent
- Trigonometric ratio for (90°-A)
- Trigonometric ratio of obtuse angles
- Trigonometric ratio for (180°-θ)
- Linear gradients and tanθ
- Correlation of trigonometric ratios of obtuse angles
- Sine formula
- Cosine formula
- Sine formula and cosine formula
- Formula for the area of a triangle
- 04 Trigonometric Functions
- General angles
- Radian system
- Arc length and area of a sector
- Trigonometric functions
- Correlation of trigonometric functions
- asinθ and acosθ graphs
- sinkθ and coskθ graphs
- sin(θ-p) and cos(θ-q) graphs
- tanθ graphs
- Properties of trigonometric functions
- Equations and inequalities involving trigonometric functions
- Addition theorem for trigonometric functions
- Double-angle formulas
- Half-angle formulas
- Composite trigonometric functions
- Formulas for sums and products
- 05 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
- Exponentiation
- Laws of exponents
- Expanding exponents (1)
- Expanding exponents (2)
- Calculations using the laws of exponents
- Significant digits
- Real-life uses of exponents
- Exponential function graphs
- Uses of exponential functions
- Equality relationship and magnitude relationship for bases of the same number
- Equality and magnitude relationships of exponents that are the same number
- Exponential equations
- Exponential inequalities
- Uses of exponential equations and exponential inequalities
- Relation between exponents and logarithms
- Properties of logarithms
- Change-of-base formula
- Logarithmic function graphs
- Properties and magnitude of logarithmic functions
- Logarithmic equations & logarithmic inequalities
- Common logarithms
- 06 Equations of Lines and Circles
- Internal division and external division
- Points on a plane (1)
- Points on a plane (2)
- Equation of a line
- Relation of 2 lines (1)
- Relation of 2 lines (2)
- Relation of 2 lines (3)
- Distance between points and lines
- Equations for circles (1)
- Equations for circles (2)
- Circles and lines (1)
- Circles and lines (2)
- 2 circles (1)
- 2 circles (2)
- Loci and equations (1)
- Loci and equations (2)
- Domains expressed by inequalities (1)
- Domains expressed by inequalities (2)
- Domains expressed by inequalities (3)
- Domains expressed by inequalities (4)
- Domains expressed by inequalities (5)
- 07 Formulas and Proofs
- Formulas for expanding cubic polynomials
- Formulas for factorizing cubic polynomials
- Binomial theorem
- Use the binomial theorem to expand equations
- Multiplication and division of fractional expressions
- Addition and subtraction of fractional expressions
- Problems to find the values of sums and products
- Dividing integer polynomials
- Dividing integer polynomials and the remainder theorem
- Factor theorem and factorizing cubic polynomials
- Identities
- How to determine constants in identities
- Proving equalities
- Proving inequalities
- 08 Advanced Expressions and Functions
- Parametrization of a curve
- Parametrization by using trigonometric functions
- Polar and cartesian coordinates
- Polar equations
- Equations using polar equations and cartesian coordinates
- Fractional function graphs
- Fractional function graphs and common points of lines
- How to solve fractional inequalities
- Irrational function graphs
- Irrational function graphs and common points of lines
- How to solve irrational inequalities
- Inverse functions and composite functions
- 09 Complex Numbers
- Equality of irrational numbers
- Imaginary units i and complex numbers
- Determining solutions to quadratic equations
- Relation between solutions and coefficients
- Problems to find the values by the relation between solutions and coefficients
- Methods to solve higher-order equations
- Relation between solutions and coefficients in cubic equations
- Complex numbers
- The complex number plane
- Polar form of complex numbers
- Multiplying & dividing polar forms
- De Moivre's theorem
- The n-th root of complex numbers
- Plane figures and complex numbers
- 10 Sequences
- Sequences
- Arithmetic progression
- Sums of arithmetic progressions (1)
- Sums of arithmetic progressions (2)
- Geometric progressions
- Sums of geometric progressions (1)
- Sums of geometric progressions (2)
- Summation symbol Σ
- Progression of differences
- Sums and general terms of sequences
- Sums of various sequences (1)
- Sums of various sequences (2)
- Grouping sequences
- Recurrence formula (1)
- Recurrence formula (2)
- Various recurrence formulas (1)
- Various recurrence formulas (2)
- Various recurrence formulas (3)
- | Mathematical induction (1)
- Mathematical induction (2)
- 11 Vectors
- Vectors
- Vector operations
- Components of vectors
- Vector operations with components
- Deformation of vectors
- Parallel vector conditions
- Vector resolution
- Inner products of vectors
- Calculating angles formed by vectors
- Perpendicular vector conditions
- How to find perpendicular vectors
- Properties of inner products
- Position vectors, and internal dividing points and external dividing points
- Position vectors of the midpoint and center of gravity
- Conditions of figures
- Formula for the area of a triangle
- Spatial vectors
- Spatial coordinates
- Components of spatial vectors
- Internal dividing points and external dividing points
- Inner products of spatial vectors
- Outer products of vectors
- 12 Statistics
- Class and frequency
- Histograms
- Relative frequency
- How to describe the characteristics of data distribution
- How to use data
- Relative frequency and probability
- Quartiles and box-and-whisker plots
- Using histograms and box-and-whisker plots
- Distribution of data
- Data correlation
- 13 Sets
- Sets and elements
- Intersections, unions, and complements
- Intersections and unions of inequalities
- De Morgan's laws
- The problem of finding various sets
- Propositions: True/false and counterexamples
- Necessary conditions and sufficient conditions
- Negation of conditions
- Negations of “And” and “Or”
- Converse, inverse, and contraposition
- Proofs using contraposition
- Proofs using contradictions
- 14 Probability
- Number of cases
- Law of addition and law of multiplicationv
- Permutations
- Various permutations
- Circular permutations
- Repeated permutations
- Combinations
- Total number of groups
- Permutations containing similar things
- Shortest path
- Repeated combinations
- Numbers of sets and elements
- Events and probability
- Probabilities of various events
- Basic properties of probability (1)
- Basic properties of probability (2)
- Basic properties of probability (3)
- Probability of independent trials
- Probability of repeated trials (1)
- Probability of repeated trials (2)
- Conditional probability
- Calculating probability
- Expected value
- 15 Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus
- Average rate of change
- Limit values
- Differential coefficients
- Derivatives
- Properties of derivatives
- Equations of tangents
- Increasing/decreasing of functions and their local maximum/minimum (1)
- Increasing/decreasing of functions and their local maximum/minimum (2)
- Increase/decrease of functions and applicable graphs (1)
- Increase/decrease of functions and applicable graphs (2)
- Increase/decrease of functions and applicable graphs (3)
- Indefinite integrals
- Properties of indefinite integrals
- Properties of definite integrals
- Definite integrals and differential calculus
- Definite integrals and the area of a shape (1)
- Definite integrals and the area of a shape (2)
- Definite integrals and the area of a shape (3)
- Definite integrals and the area of a shape (4)
- Definite integrals and the area of a shape (5)
- 16 Limits
- Limits of sequences (convergence, divergence, and oscillation of infinite sequences)
- Squeeze theorem
- Limits of infinite geometric sequences
- Recurrence formula and limits
- Convergence and divergence of infinite series
- Convergence and divergence of infinite geometric series
- Properties of infinite series
- Limits of functions
- Limits of functions (indeterminate form)
- One-sided limits
- Limits of various functions and Napier’s number e
- Continuity of functions
- Intermediate-value theorem
- 17 Advanced Differential Calculus
- Product-quotient differentiation
- Differentiation of composite functions
- Differentiation of trigonometric functions
- Differentiation of exponential functions ex
- Differentiation of logarithmic functions
- Differentiation of exponential functions ax
- Differentiation of the function xp
- High-order derivatives
- Differentiation of implicit functions
- Differentiation of functions expressed as parameters
- Differentiation of logarithms
- Equation for a tangent
- Equation for a normal line
- Function increase/decrease and derivative signs
- Maximums and minimums of functions
- Maximum and minimum values of functions
- Concavity, convexity and inflection points of curves
- How to draw graphs of functions
- 2nd-order derivatives and extrema
- Proving inequalities
- Number of real roots of equations
- 1st order approximation of a function f(x)
- Product-quotient differentiation
QR Code Link Feature
The teaching materials were developed to communicate the appeal of scientific calculators to teachers and students. They aim to change awareness and enhance learning efficiency in mathematics by minimizing time spent on manual calculations, reducing aversion to complex math. These materials also promote diversification in learning and problem-solving methods, particularly beneficial for real-life scenarios with complex values. Lastly, creative use of various calculator functions facilitates a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts, encouraging exploratory learning and visualization of numerical values through tables without the need for listing or numbering.
Input data

Generate & scan QR code

Graph on smart device
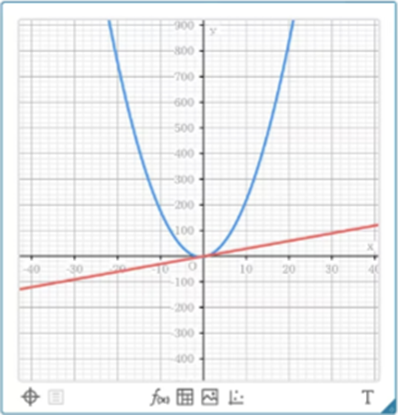
Makes formulas visually understandable
Analyze graph

Classpad.net allows you to display graphs and perform various visual analyses
How to Get CASIO ESSENTIAL MATERIALS
If you register with CASIO ID MEMBERS, you can download CASIO ESSENTIAL MATERIALS for free.
*If you are not registered with a CASIO ID MEMBERS, you will not be able to download CASIO ESSENTIAL MATERIALS.
CASIO Essential Materials
Publisher : CASIO Institute for Educational Development
Date of Publication : 2023/11/10 (1st edition)
Copyright © 2023 CASIO COMPUTER CO., LTD.
(1) Teachers may freely copy and distribute materials for use by students and in classes only.
*However, publishing on the web or sending all at once to an unspecified number of people is prohibited.
(2) If you wish to copy, edit, distribute, or use the content for purposes other than those listed above, permission from Casio Computer Co., Ltd. is required.